The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 dramatically increases the Internal Revenue Code (IRC) Section 179D energy-efficient commercial building deduction, making it especially impactful for the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industries as well as commercial building owners.
The act was signed by President Joe Biden on August 16, 2022.
Outline of IRC Section 179D Changes
These changes are significant and add additional value—and complexity—to IRC Section 179D. They apply to qualifying property placed in service after December 31, 2022.
Who’s Eligible?
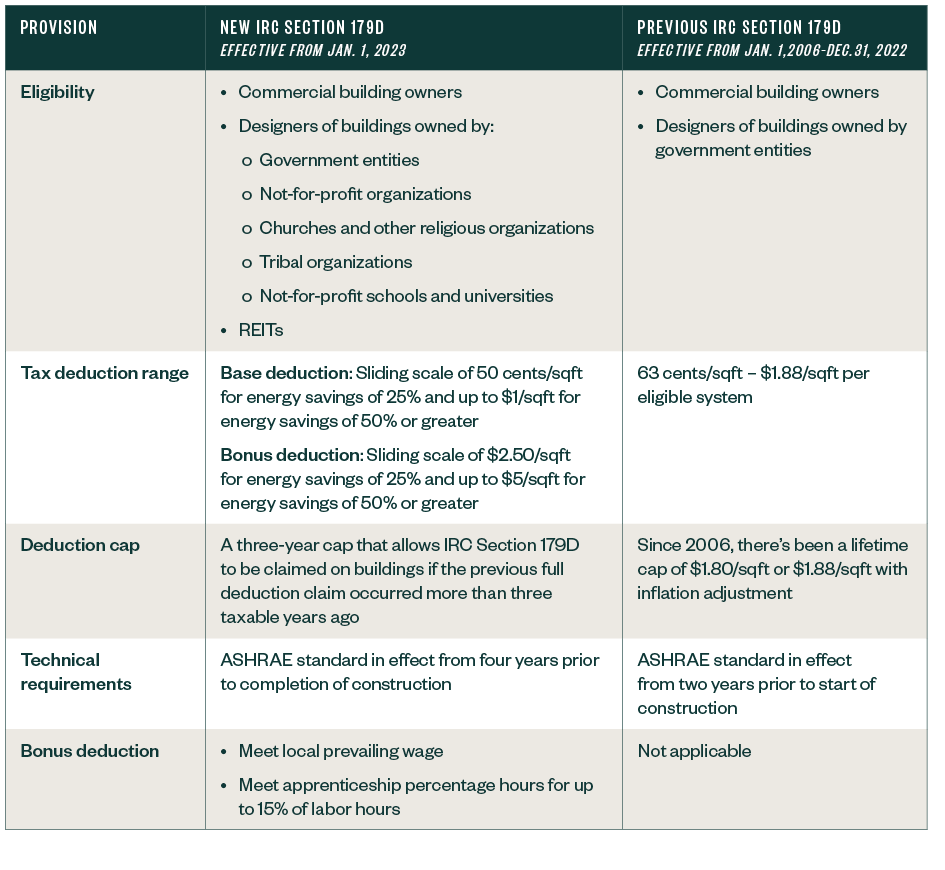
The Inflation Reduction Act extends the deduction to designers of commercial buildings owned by tax-exempt entities, including not-for-profit organizations, churches and other religious organizations, tribal organizations, and not-for-profit schools and universities.
This is in addition to current eligibility, which only includes commercial building owners and designers of buildings owned by government entities.
The new provisions in the act expand eligibility for companies claiming IRC Section 179D to include REITs, which are companies that own, operate, or finance income-producing real estate across various property sectors.
Increases Qualification Thresholds
The act sets the qualification threshold for deductions at 25% energy cost savings, with a base deduction equal to 50 cents per square foot (sq ft) and bonus deduction equal to $2.50/sq ft.
Additionally, it increases the deduction on a sliding scale for each percentage point above 25% when energy usage is reduced. This increase is capped at a 50% reduction with the base deduction set at $1/sq ft and bonus deduction equal to $5/sq ft.
Previously, the tax deduction range was 63 cents/sq ft for each of the three eligible systems, including HVAC and hot water, interior lighting, and building envelope to a maximum value of $1.88/sq ft.
Adds Bonus Deduction
The bonus deduction previously mentioned is available to companies that meet local prevailing wage and apprenticeship requirements for any laborers and mechanics employed by the taxpayer or contractors associated with the installation. This is a wholly new addition.
Updates ASHRAE Standard Requirements
The act now states that projects must be measured against the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) standard from four years prior to completion of construction.
This is a change from previous provisions, which is the ASHRAE standard in effect from two years prior to the start of construction.
Creates Alternate Deduction Path
The act creates an alternate deduction path for renovation projects based on reducing a building’s energy-use intensity by 25% or more.
Compare Previous Versus Updated IRC Section 179D Provisions
The additional value and complexity of the changes to IRC Section 179D are demonstrated in the table below, which summarizes the previous state of IRC Section 179D and the changes made by the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022.
IRC Section 179D Comparison Table
How to Mitigate Risk with IRC Section 179D Changes
As part of the act, the IRS will gain an additional $80 billion of funding, much of which will go toward enforcing tax compliance amid the changing tax-code environment.
This makes it important to choose an IRC Section 179D provider who understands the risks, can help mitigate IRS actions, and possesses the technical knowledge to perform compliant IRC Section 179D studies.
We’re Here to Help
To learn more about how provisions in the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 could impact your business, contact your Moss Adams professional. You can also see the most updated tax planning strategies related to these changes on our Tax Planning Resources page.