
For businesses growing via acquisition or operating in different industries or business areas, implementing a two-tier ERP system can be a game-changer. Companies with this multi-entity structure may need to form or maintain subsidiaries or business units that operate independently, each with its own set of unique requirements.
A two-tier ERP system can help to streamline operations across the organization and allow each entity to operate a system that is a good fit for its unique business while allowing visibility and reporting at a corporate level.
By adopting this approach, each business aligns its various operations with the system it will use while also providing information corporate needs to support the overall business.
This article explores the benefits of a two-tier ERP system for businesses that grow via acquisition, and why it may be the right choice for your organization.
What’s a Two-Tier ERP?
A two-tier structure is an approach to ERP systems that involves using two different ERP systems at the same time.
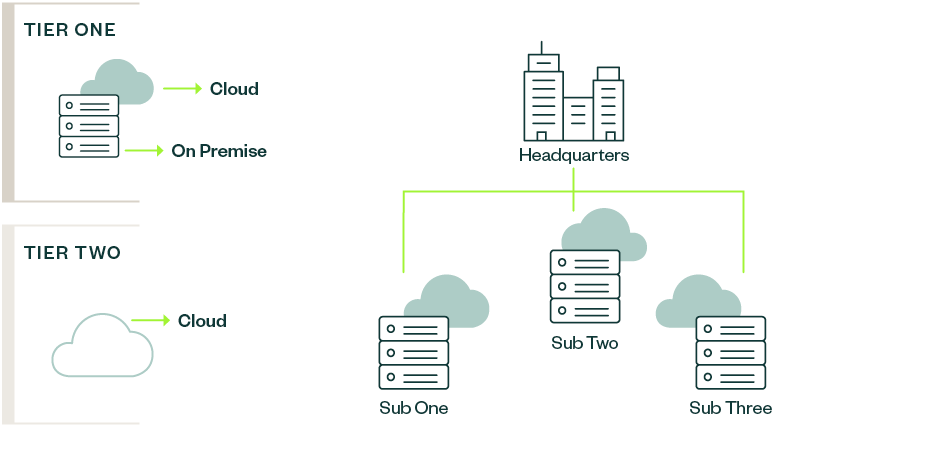
The first system is typically a larger, more comprehensive ERP system used at the corporate or headquarters level. The second system is a smaller, more specialized ERP system that is used at the subsidiary or division level.
The two systems are integrated so that data can be shared between them, but each system is designed to meet the specific needs of its users. This approach is often used by companies with multiple subsidiaries or divisions that have different business processes and requirements.
Why Use a Two-Tier ERP Strategy?
Following are some common use cases for a two-tier ERP strategy.
Parent Company ERP Doesn’t Fit Subsidiaries
If a parent company runs a large, complex ERP system that meets the needs of a large, complex business while its subsidiaries are smaller and less complex, then a two-tier system structure allows each entity to use a system that is right-sized without forcing complexity, costs, and IT overhead on smaller companies or business units.
Global Companies
Global companies with multiple subsidiaries or locations around the world often have different business processes and requirements in each location.
A two-tier ERP strategy can help ensure that each location has the specific functionality and support it needs, while still allowing for centralized management and reporting.
M&A
Companies that have undergone mergers or acquisitions may have multiple ERP systems in place that need to be integrated.
A two-tier ERP strategy can help integrate with the larger, more comprehensive ERP system used at the corporate or headquarters level.
Specialized Business Units
Companies with specialized business units, such as manufacturing or distribution, may have unique requirements that are not fully supported by a single, comprehensive ERP system.
A two-tier ERP strategy can give each business unit needed specific functionality and support.
Rapidly Growing Companies
Companies that are rapidly growing may find that a single, comprehensive ERP system is not scalable enough to meet their needs. A two-tier ERP strategy can give each location specific functionality and support it while allowing for centralized management and reporting.
Cost-Conscious Companies
Companies watching spending might find a two-tier ERP strategy is more cost-effective than implementing a single, comprehensive ERP system for all locations.
Allowing each location to use a smaller, more specialized ERP system can reduce costs while supporting specific functionality.
What Are the Benefits?
Following are some benefits of a two-tier ERP system structure.
Flexibility
A two-tier ERP system structure allows companies to choose the best ERP system for each subsidiary or division based on specific requirements, allowing greater flexibility and agility.
Cost Savings
A smaller, more specialized ERP system at the subsidiary or division level can often save money compared to using a more comprehensive system for all operations.
Improved Efficiency
A two-tier ERP system allows each subsidiary or division to use the ERP system best suited to streamlining its processes.
Better Data Management
By integrating the two ERP systems, companies can ensure that data is shared between them in a consistent and accurate manner, which can help improve data management and decision-making.
Faster Implementation
A smaller, more specialized ERP system at the subsidiary or division level can be implemented more quickly than a comprehensive system for all operations.
Choose an ERP for a Two-Tier Strategy
Consider each of these factors when choosing a system.
Define Requirements
Start by defining the specific requirements of each subsidiary or division. This includes identifying the business processes that need to be supported, the data that needs to be managed, size and complexity of the business unit or subsidiary, and the reporting and analytics needs of both the parent and child companies.
Evaluate Vendors
Research ERP vendors that offer solutions for the specific needs of each subsidiary or division. Consider factors such as the vendor's experience in your industry, the scalability of the solution, cost of the solution including acquisition, implementation, and operation, and the level of support and training offered.
Consider Integration
Look for ERP systems that can integrate with the larger, more comprehensive ERP system used at the corporate or headquarters level so data can be shared consistently and accurately between the two systems.
Evaluate Costs
Look for solutions that offer a good balance between functionality and cost of acquisition, implementation, and maintenance.
Consider User Experience
Look for systems that are easy to use. Can users quickly find the information they need? Does it provide easy access to the information for each user role to perform their daily tasks? Evaluate the overall ease of use and efficiency of performing tasks within the system as well as how much process automation it can bring to the business.
Validate the Solution
Before making a final decision, bring in key stakeholders and end users to validate the ERP system to ensure that it meets the specific needs of each subsidiary or division. Change management and user buy-in is central to the success of any software project success.
Why NetSuite?
NetSuite can be a good choice in a two-tier ERP strategy for several reasons.
Flexibility
NetSuite is highly customizable, allowing companies with multiple subsidiaries or locations with different business processes and requirements to meet the diverse needs of the businesses.
Integration
NetSuite supports a two-tier strategy because it offers a full integration platform as part of the software, allowing it to work and share data with other ERP systems.
Functionality
NetSuite is a full ERP and offers a wide range of functionality, including financial management, inventory management, order management, and more, supporting companies with specialized business units and unique requirements. It also has industry-specific versions tailored to key industries that allow it to better meet the needs of your business.
Cloud Based
NetSuite is a cloud-based ERP system, which makes it easy to deploy and manage across multiple locations. Companies with multiple subsidiaries or locations can manage IT costs and complexity.
User Friendly
NetSuite has a user-friendly interface and role-based security and reporting increasing the ease of use and driving higher adoption from users across your organization.
A customizable cloud-based enterprise resource planning (ERP) system like NetSuite can help companies to meet the specific needs of each subsidiary or location while still allowing for centralized management and reporting.
We’re Here to Help
For guidance on selecting and implementing NetSuite or any ERP system for your organization, contact your Moss Adams professional.
Additional Resources
About NetSuite
From fast-growing startups to global enterprises, NetSuite powers businesses across a variety of industries. NetSuite provides cloud financials, customer relationship management (CRM), e-commerce, human capital management (HCM), and professional services automation management for all organizations from fast-growing midsize companies to large global organizations. Additionally, each component of NetSuite is modular, enabling it to be deployed and integrated with existing investments as required.
With more than 36,000 customers running NetSuite worldwide and dependent territories, some of the world's most innovative organizations trust NetSuite and take their financial and operational processes to the cloud.